
Universal Pumping | High Pressure Pumps
High Pressure Pumps for Difficult to Pump Slurry, Sludge, and Food Waste.
A piston pump is a vital component in various industries, renowned for its efficiency and reliability. According to John Smith, a leading expert in hydraulic machinery, "Piston pumps provide precise control over fluid flow." This highlights the importance of understanding how these pumps operate and their applications.
Piston pumps work through a simple yet effective mechanism. They use a piston to create suction and pressure, drawing liquid and forcing it out. This design allows for a consistent flow of fluid. In applications like oil extraction or water supply systems, piston pumps ensure that operations run smoothly.
However, users often overlook maintenance issues. Neglecting regular check-ups can lead to reduced efficiency. A piston pump may fail to deliver expected performance due to wear and tear. Recognizing these flaws is essential for maximizing pump longevity. Understanding the intricacies of piston pumps is key to harnessing their full potential.
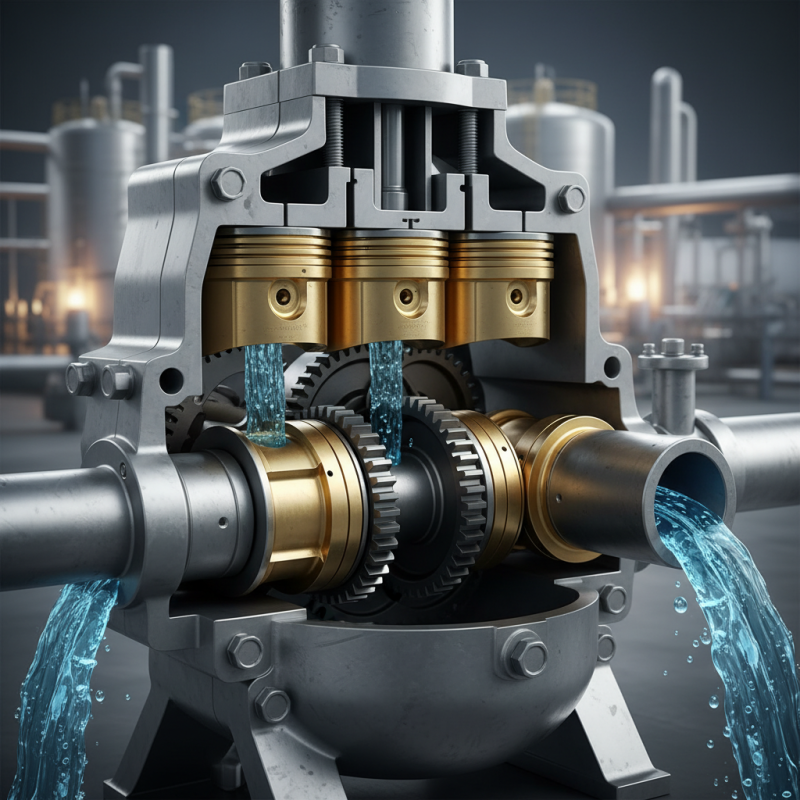

A piston pump is a type of positive displacement pump. It uses a piston to move fluid through a cylinder. This movement creates a vacuum that draws fluid into the chamber. As the piston moves back, the fluid is pushed out. This action is simple but very effective.
The design of a piston pump can vary. Some are single-acting, using one side of the piston. Others are double-acting, utilizing both sides. Each type has its pros and cons. For instance, single-acting pumps tend to be less complex. However, double-acting models are often more efficient. This is not always the case, though. Efficiency can depend on the application.
Understanding how a piston pump works is essential. It finds uses in various industries, from automotive to agriculture. However, maintenance is crucial for optimal performance. Piston wear can lead to leaks or reduced efficiency. Regular checks help to ensure long-term operation. Sometimes, people overlook these details, leading to failures. It’s important to reflect on how these choices impact overall performance.
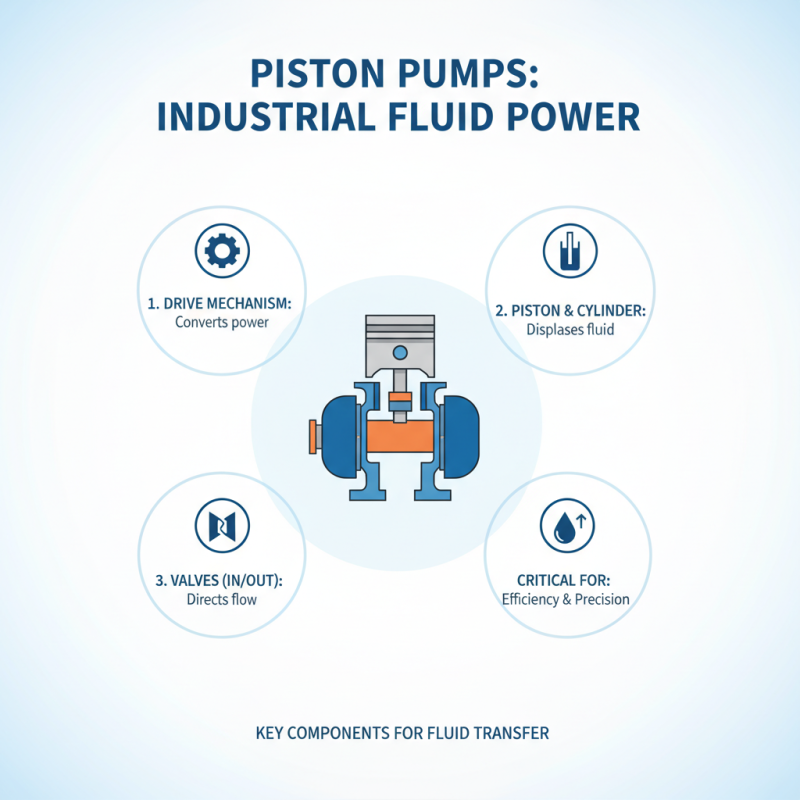
Piston pumps are critical in various industries, leveraging mechanical action to move fluids. Their efficiency largely depends on their components, which require precise design and operation. The main components include the piston, cylinder, valves, and drive mechanism.
The piston is usually cylindrical and moves back and forth within the cylinder. This movement creates pressure changes that draw fluid in and push it out. Valves control the fluid's entry and exit, ensuring one-way flow. According to recent industry reports, piston pumps can achieve up to 90% efficiency under optimal conditions. However, improper installation can lead to leaks, reducing performance.
Drive mechanisms can vary, often using electric motors or internal combustion engines. These systems generate the force needed for the piston’s movement. A study indicates that regular maintenance can extend piston pump life by over 30%. Yet, misalignment issues or wear can significantly hinder their function. Understanding these components helps in troubleshooting and enhancing performance.
Piston pumps are vital components in various industries. They work by converting linear motion into fluid movement. The core mechanism involves a piston moving within a cylinder, creating pressure differentials to draw fluid in and push it out. When the piston moves down, it creates a vacuum, allowing fluid to enter. As it moves up, the fluid is expelled, maintaining a continuous flow.
Piston pumps are commonly used in hydraulic systems. According to the Hydraulic Institute, they are capable of achieving high pressures and flow rates. This makes them suitable for applications such as lifting heavy loads or transferring fluids across long distances. A typical piston pump can achieve pressures of up to 10,000 psi, depending on the design and materials used.
Tip: Regular maintenance of piston pumps is crucial. This includes checking the seals and lubricating the moving parts to prevent wear and tear. Overlooking these details can lead to inefficiencies or failures, increasing downtime and costs.
Precision is key. Exact alignments in the pump assembly can enhance performance. Ensure that the piston and cylinder are well-fitted to avoid issues. A slight misalignment can greatly affect the pump's efficiency, leading to lower output and increased energy consumption. Always prioritize careful assembly and inspections.
| Dimension | Value |
|---|---|
| Pump Type | Piston Pump |
| Operating Principle | Positive Displacement |
| Common Applications | Hydraulic systems, Water supply, Fuel injection |
| Efficiency | High efficiency with minimal leakage |
| Flow Rate | Variable (depending on size and speed) |
| Pressure Output | Up to several thousand PSI |
| Maintenance | Regular checks for wear and seals |
| Advantages | Compact design, precise flow control, ability to generate high pressure |
| Disadvantages | Possible maintenance challenges, pulsating flow |
Piston pumps play a vital role in various industries due to their efficiency and reliability. In the oil and gas sector, these pumps are commonly employed for hydraulic fracturing, a process essential for extracting natural resources. According to a report by the U.S. Energy Information Administration, the hydraulic fracturing market is expected to reach $50 billion by 2025. This growth illustrates the ongoing demand for piston pumps in resource extraction.
In the manufacturing industry, piston pumps are used for precise fluid control. Their ability to deliver consistent pressure makes them suitable for applications like paint spraying and lubrication systems. A market analysis by Technavio highlights that the global industrial pump market will grow at a CAGR of 5% from 2021 to 2025. This trend indicates a rising reliance on piston pumps in industrial operations.
However, challenges remain. Piston pump maintenance can be costly and time-consuming. Issues like wear and tear can affect performance, leading to downtime. It's crucial for companies to invest in regular maintenance to avoid these problems. Despite their advantages, piston pumps may not always be the most cost-effective option in every scenario. Balancing performance and operational costs is an ongoing conversation in the industry.
Piston pumps offer several advantages that make them popular in various industries. Their robust design allows them to handle high pressure and deliver a consistent flow rate. According to a recent industry report, piston pumps can achieve pressures up to 5000 psi. This capability makes them ideal for applications like hydraulic systems and water jet cutting.
Their efficiency in transferring fluids is another significant advantage. They can maintain a high mechanical efficiency, often exceeding 90%.
However, piston pumps also have limitations. One major drawback is their maintenance needs. Regular servicing is crucial to ensure they operate smoothly. Failure to service can lead to wear and excessive vibrations. This impacts both performance and longevity. Additionally, piston pumps can be less efficient when handling certain viscosities. Fluids with high viscosity may cause cavitation, affecting pump efficiency. Ultimately, these factors need consideration for long-term use.
Noise is another concern. Piston pumps can be quite loud during operation. A study found that they can generate noise levels above 85 decibels. This aspect may require users to implement noise reduction strategies. Evaluating these advantages and limitations is essential for choosing the right pump for specific applications.




Universal Pumping
625 Apache Trail
Woodstock, GA 30189
Mon - Fri | 9:00 AM - 5:00 PM
Universal Pumping is staffed with industry professionals with 20-45 years experience with high pressure pumping systems. We represent only the “elite producers” in pump manufacturing: Britain’s EMS and Germany’s EMMERICH. Our engineering and manufacturing approach is conservative, and we do not use “guess work” in the design or sales of our pumping and filtration equipment.



