
Universal Pumping | High Pressure Pumps
High Pressure Pumps for Difficult to Pump Slurry, Sludge, and Food Waste.
A sand pump is an essential tool in various industries. It efficiently transports sand and aggregates with precision. According to a recent study by Grand View Research, the global sand pump market is projected to reach $2.2 billion by 2027. This growth highlights the increasing demand for reliable sand handling solutions in construction and mining sectors.
Understanding how a sand pump works is crucial. Sand pumps utilize centrifugal forces to move materials through pipelines. They can handle different types of sand, from fine grains to coarse aggregates. However, not all sand pumps are created equal. Each design has its own advantages and drawbacks, making it vital to choose the right type for specific applications.
Despite advances in technology, challenges still exist in the selection and maintenance of sand pumps. Issues such as wear and clogging can arise, affecting efficiency and productivity. Often, operators may overlook the importance of routine maintenance, leading to increased downtime. An informed approach is necessary. A deeper understanding of sand pump operations can lead to better performance and prolonged lifespan.
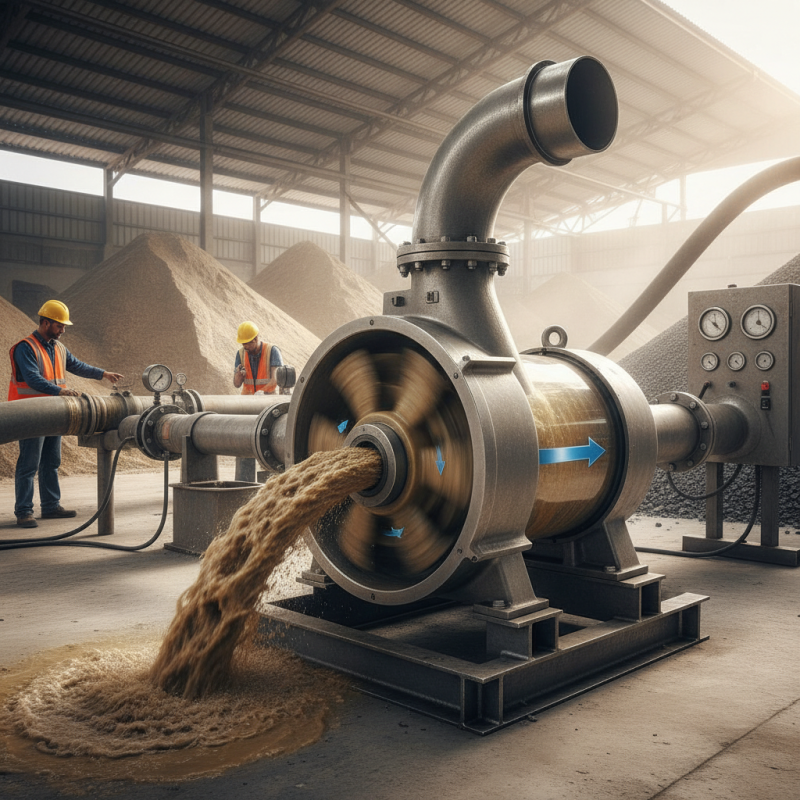

A sand pump is a mechanical device designed to move sand and similar abrasive materials. These pumps are crucial for various applications, including construction and dredging. The primary function is to transfer materials from one place to another efficiently. Sand pumps usually work by creating a vacuum, which draws sand into the pump.
When using a sand pump, it's essential to consider the type of material being transported. The composition and size of the sand particles can affect the pump's efficiency. Maintenance is equally important. Regular checks can prevent wear and improve longevity.
**Tip:** Always inspect the pump after use. Look for signs of wear or damage.
Additionally, the placement of the pump matters. If positioned incorrectly, it may not draw the sand effectively. Understanding the pump's specifications can help you choose the right design for your needs.
**Tip:** Consult with experts before purchasing. Proper advice can save you from costly mistakes.
A sand pump may seem straightforward, but using it requires attention to detail. Erroneous setups can lead to inefficient operations. It's worth reflecting on the setup and environmental conditions to optimize performance.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Type | Positive Displacement Pump |
| Common Uses | Construction, Mining, Dredging |
| Typical Materials Pumped | Sand, Gravel, Slurries |
| Operating Principle | Moves material by creating a pressure difference |
| Advantages | Efficient in handling abrasive materials, Durable |
| Limitations | Requires regular maintenance, Can be heavy |
| Pump Size Variability | Available in various sizes to suit different applications |
| Energy Source | Electricity, Diesel, Hydraulic |
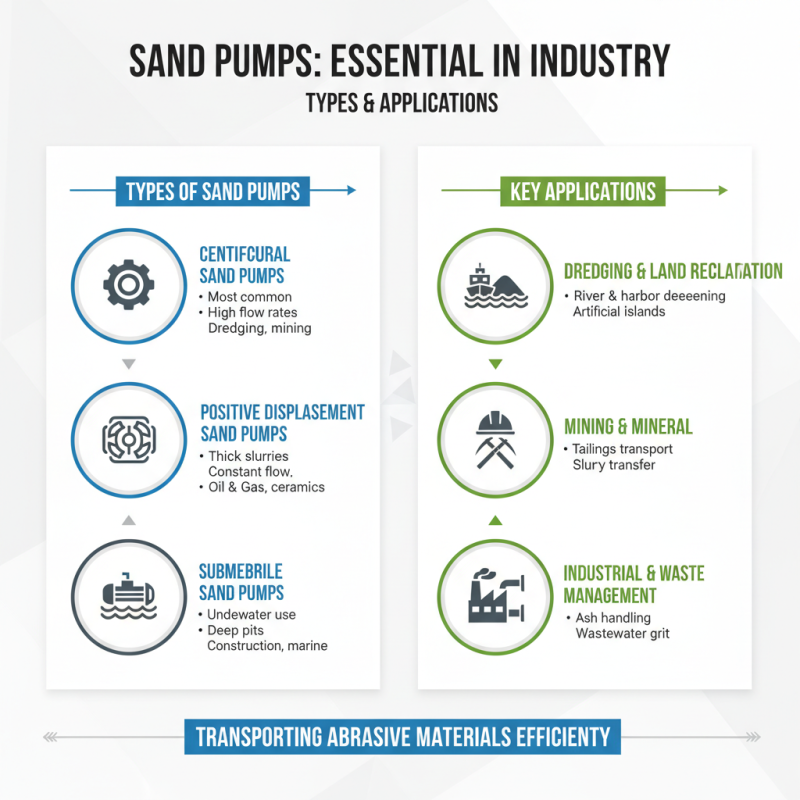
Sand pumps are essential in various industries. They are primarily used for transporting sand and other abrasive materials. Understanding the types of sand pumps is crucial for effective applications.
There are three main types of sand pumps. First, there are centrifugal pumps. These are commonly used in construction and mining. They can handle mixtures of water and sand efficiently. According to a recent industry report, centrifugal sand pumps have a market share of over 40%. Their ability to sustain high flow rates makes them a preferred choice in many applications.
Next, diaphragm pumps are popular in dredging. These pumps can operate under challenging conditions. They can handle thick slurries without the risk of clogging. Reports indicate that the diaphragm pump segment is growing rapidly, with a projected CAGR of 5% over the next five years. Lastly, submersible sand pumps are frequently used in well drilling. They work underwater and can transport sand directly to the surface. However, they require a careful approach to avoid overheating during operation.
Each type serves unique purposes, and their effectiveness depends on specific project needs. Evaluating the best pump for a task is vital. Understanding limitations can prevent operational issues.
A sand pump is a specialized tool for moving sand and sediment. It operates by creating a vacuum or using pressure to pull material into its chamber. This mechanism is crucial in various industries, such as construction and mining. The simple design allows for effective transport without damaging the particles.
When a sand pump operates, it typically draws sand through an intake pipe. The fluidity of the sand is often enhanced with water or other mixtures. This process helps the pump move heavier materials seamlessly. However, it can also lead to clogs or inefficiencies if not monitored. Not every pump handles abrasive materials well, and wear and tear can complicate operation over time.
Users often overlook maintenance needs. Regular checks can prevent failures and prolong the pump's life. It's essential to consider the pump's capacity and limitations. Every workspace has unique challenges. Identifying these nuances can lead to better performance. Even a small oversight can disrupt the entire operation.
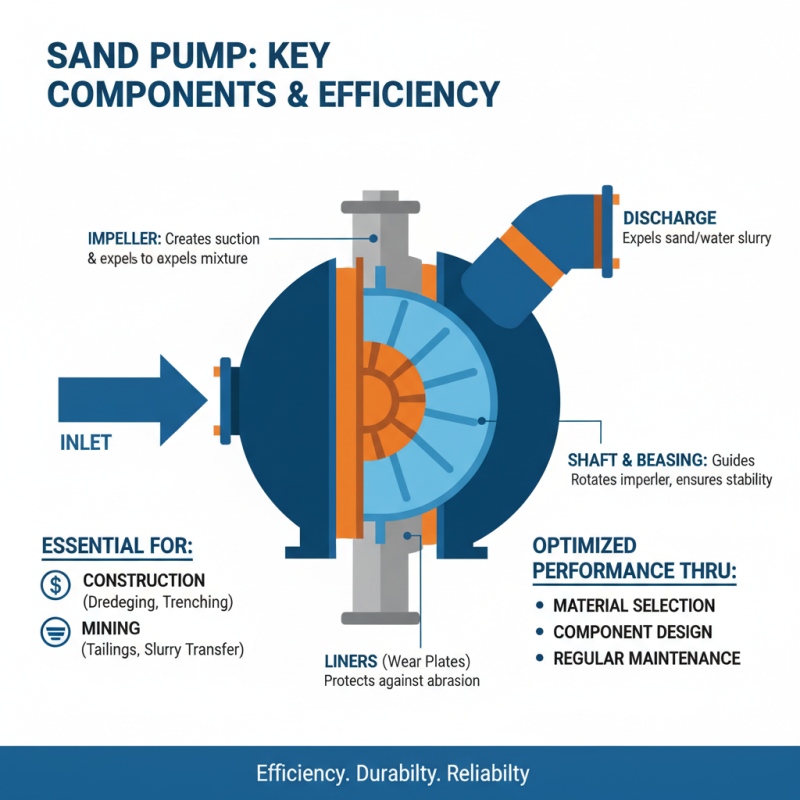
A sand pump is essential for various industries, especially construction and mining. Its design features specific components that determine efficiency and functionality. Understanding these components helps in optimizing the pump's performance.
One significant part of a sand pump is the impeller. It provides the necessary thrust to move sand and other solids. A properly designed impeller can enhance the flow rate significantly. According to industry reports, an improved impeller can increase efficiency by up to 25% in some cases. This is critical in reducing operational costs for large-scale projects.
Another key component is the casing. The casing protects the internal mechanics from wear and tear. Materials used for casings often include high-grade alloys or rubber lining. These materials must withstand harsh conditions and abrasive particles. Research indicates that inadequate casing can lead to a 30% reduction in pump life. Regular inspections can identify early signs of damage, saving significant repair costs. Exploring these components reveals much about a sand pump's overall effectiveness and longevity.
Sand pumps are essential tools in various industries, especially in construction and mining. They offer significant advantages, including efficient transfer of sand and sediment. Sand pumps are designed to handle abrasive materials effectively, which makes them crucial in dredging operations and concrete mixing. The global sand pump market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.2% from 2021 to 2026, reflecting increasing demand in emerging economies.
However, sand pumps do have limitations. One common issue is their wear and tear, especially when dealing with highly abrasive materials. Regular maintenance is essential to prolong the pump's lifespan. In some cases, their performance may decrease for larger sand particles. This can lead to inefficiencies and increased operational costs. It's important to choose the right sand pump type for specific applications.
Tips: Always monitor your pump’s performance for signs of wear. Invest in quality materials and design to minimize future issues. Custom solutions can make a notable difference in efficiency. Keep in mind that occasional setbacks in sand pump operations are normal; it is critical to adapt for better outcomes.






Universal Pumping
625 Apache Trail
Woodstock, GA 30189
Mon - Fri | 9:00 AM - 5:00 PM
Universal Pumping is staffed with industry professionals with 20-45 years experience with high pressure pumping systems. We represent only the “elite producers” in pump manufacturing: Britain’s EMS and Germany’s EMMERICH. Our engineering and manufacturing approach is conservative, and we do not use “guess work” in the design or sales of our pumping and filtration equipment.



